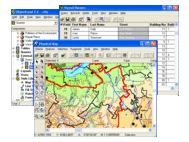
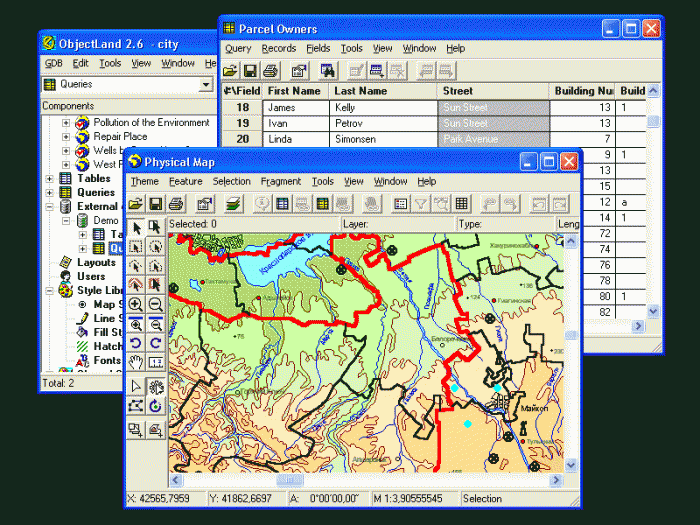
GIS ObjectLand is a universal Geographic Information System for Windows. Key capabilities: using spatial data and tables from internal database or external DBMS; multiuser data editing; import and export for MIF/MID (MapInfo), SHP (ArcView), DXF (AutoCAD), DBF (dBASE), CSV; setting access permissions to data for different categories of users; automation COM interfaces for user applications.
Publisher description
GIS ObjectLand is a universal Geographic Information System for Windows. Key features: - creation of vector-raster maps with arbitrary structure of layers and feature types in an internal ObjectLand database or in following DBMSs - MS SQL Server, Oracle, DB2, MySQL, Interbase/Firebird, PostgreSQL, MS Access; - creation of themes. Theme is a user presentation of a map; - control of displaying features depending on the chosen scale; - spatial data input and editing by assigning feature coordinates and also by interactive drawing with mouse or digitizer; - sewing of separate pages of an imported map into one unified continuous map; - copying, merging, and moving maps, layers, and feature types between different geoinformation databases; - creation of tables of arbitrary structure; - creation of queries. Query is a user presentation of table built by setting search and sorting conditions, joining tables, calculations and using reference tables; - copying, merging, and moving tables and queries between different geoinformation databases; - setting arbitrary links between spatial and table information; - getting information about the feature selected on the map; - searching for features on the map by linked records; - creation of filters. Filter is conditions of feature visualization depending on spatial properties of features and linked table data; - creation of layouts. Layout is an output form combining spatial, table information and presentation elements; - import and export of table and spatial information for widespread data formats; - support of style libraries containing fonts, map symbols, line styles, hatches and fill styles; - style editors for displaying styles; - setting for users the access permissions to components; - multiuser data editing; - using and editing tables of external database (via ODBC) as linked tables; - providing automation COM interfaces for user applications.
Related Programs

View system information tool.

Information System for companies.

Auslogics System Information 2.2.0
Detailed computer system information.

U&I Information Management System 3.1
Universal & Intelligent Infor Management

Audit network for hardware and software info.